The projects are implemened in:
• Implemented filters (including Kalman and particle filters) in order to localize moving objects
whose locations are subject to noise.
• Implement search algorithms (including A*) to plan the shortest path from one point to another
subject to costs on different types of movement.
• Implement PID controls to smoothly correct an autonomous robot’s course.
• Implement a SLAM algorithm for a robot moving in at least two dimensions.
Github Repo is private. Please contact me for if you are interested in a demo.
Developing a driverless vehicle has long been a dream for many, including myself. This project aims to assemble the necessary techniques to create an autonomous driving drone capable of reaching a target location while effectively avoiding collisions with trees.
The first algorithm explored in this project is localization, where two powerful techniques, the Kalman filter and the particle filter, are investigated. The Kalman filter, known for handling uncertainty and noise in measurements and system dynamics, combines predictions from a mathematical model with measurements to produce an optimal estimate of the system’s state.
In the following animation, an autonomous missile launching system is showcased, demonstrating its ability to shoot down meteorites. Sensor data is fed into the filter, allowing the processing of meteorite positions on a global scale.
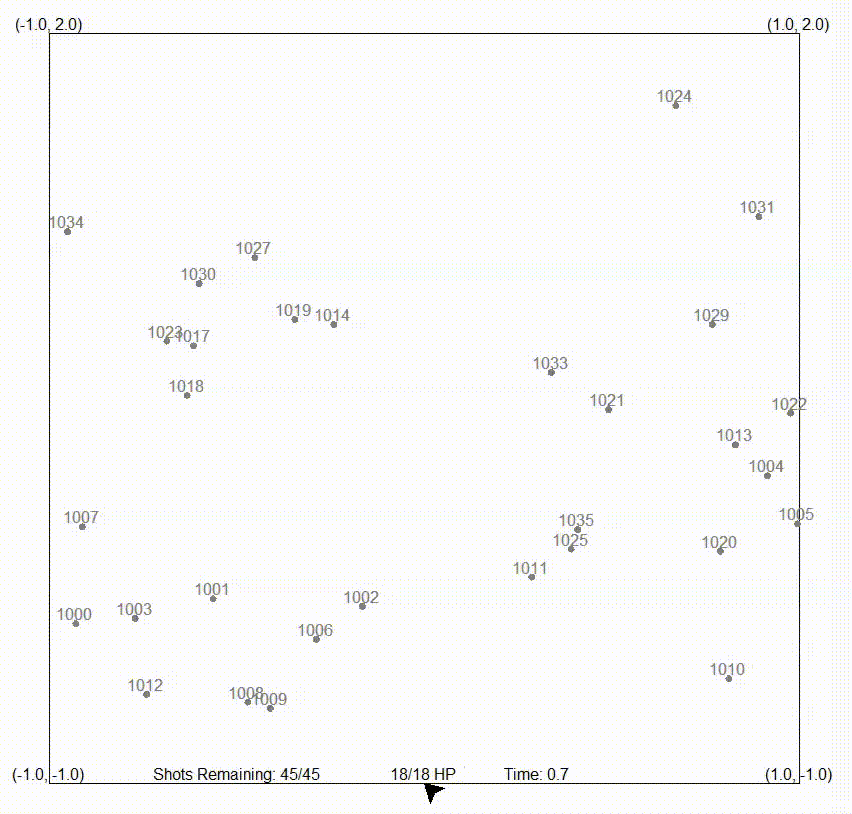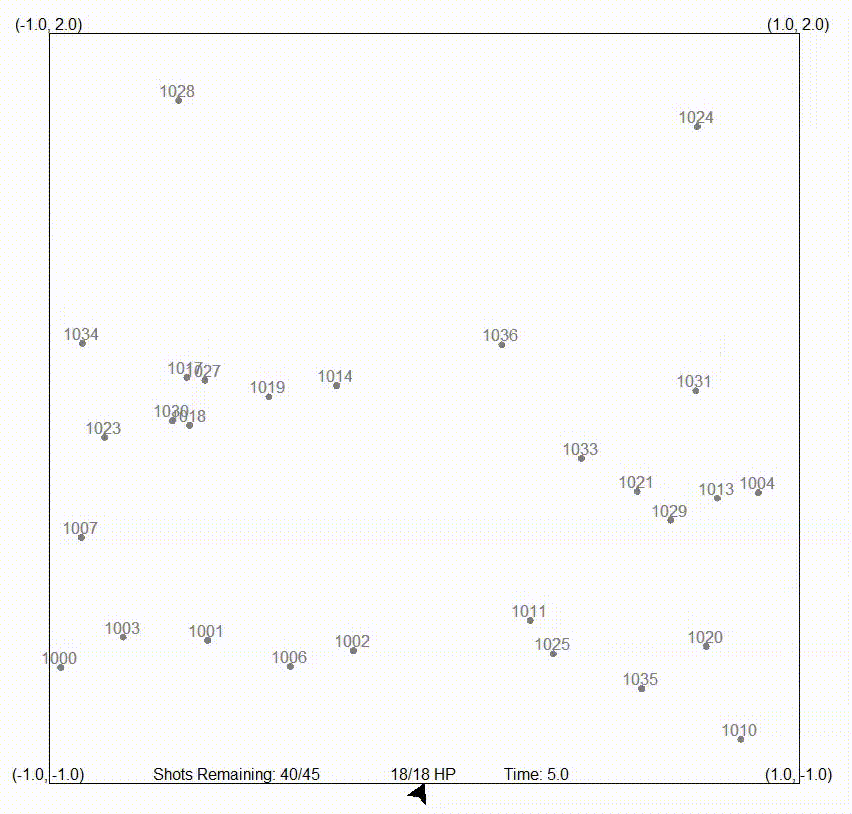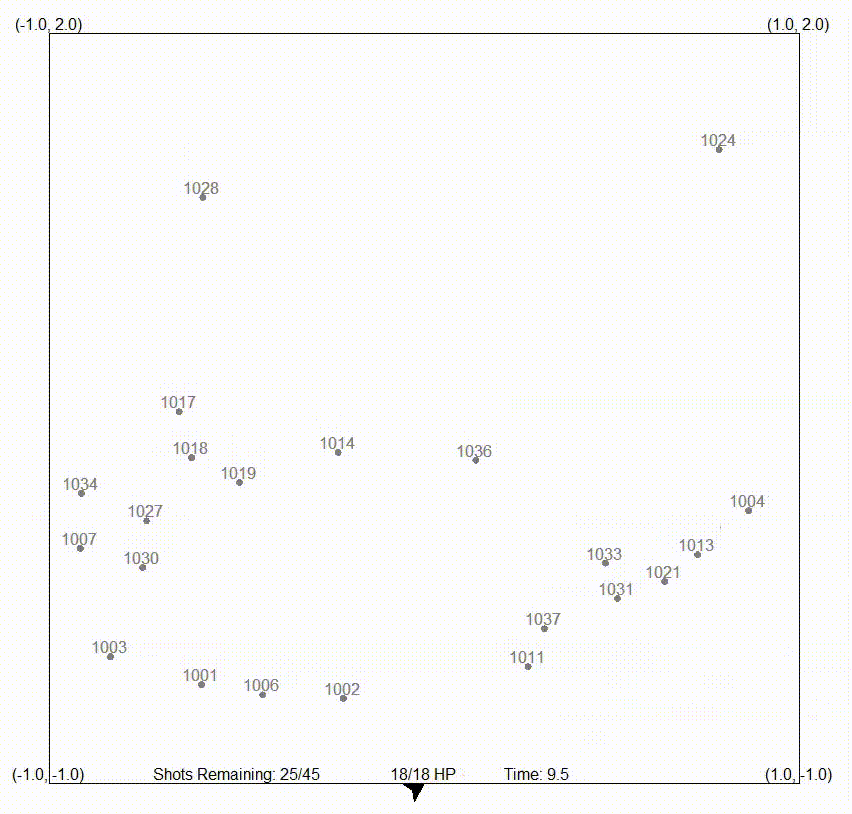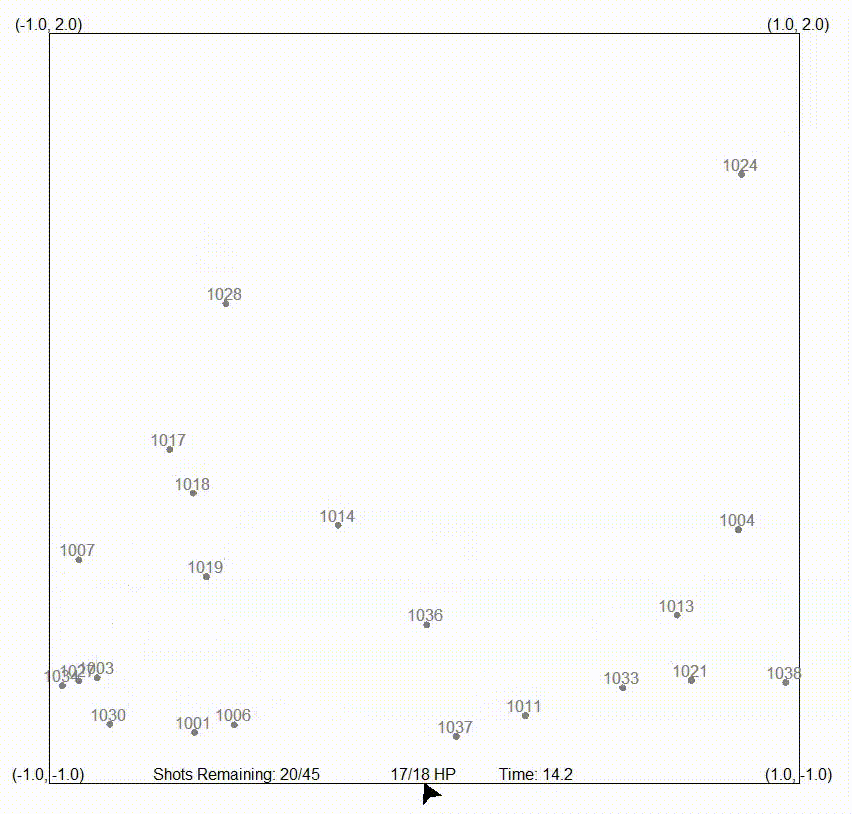
On the other hand, the particle filter, also referred to as a sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) method or a particle swarm estimator, is a recursive Bayesian filtering algorithm particularly suitable for state estimation in dynamic systems. It excels in dealing with nonlinear and non-Gaussian systems, and represents the posterior distribution of the system’s state using discrete samples called particles.
The subsequent animation visually depicts the application of a particle filter to localize a man-made satellite in a solar system.

Once an object is located, fine control of the autonomous vehicle becomes crucial. In this project, we explore the PID controller. The PID controller, widely used in engineering and industrial applications, is a feedback control mechanism that regulates and stabilizes systems. It adjusts the control output based on the error between the desired setpoint and the measured process variable.
Animation Description: The animation illustrates an optimization algorithm that assists in finding the optimal Proportional (P), Integral (I), and Derivative (D) gains for the controller.

Next, the robot needs to determine the optimal path to reach the target. For this purpose, a heuristic A* algorithm is implemented, utilizing a dynamic programming approach. Path planning plays a pivotal role in numerous navigation-based applications.
The subsequent animation offers a visualization of a robot skillfully navigating towards a box and delivering it to the target location, showcasing the significance of the path-planning algorithm.
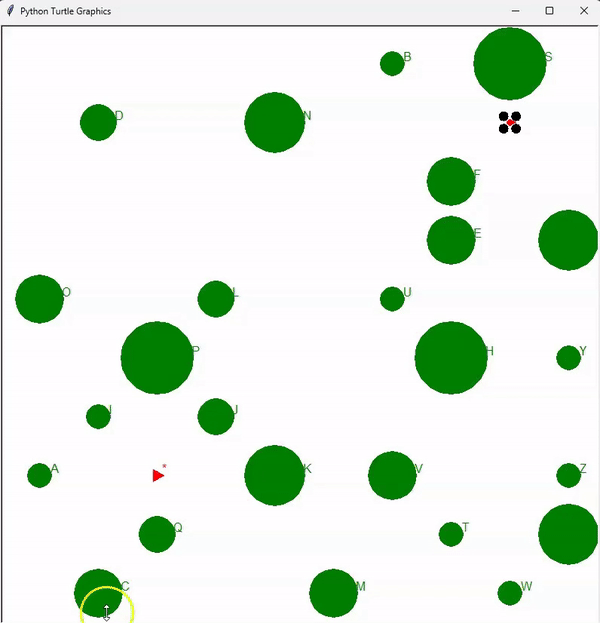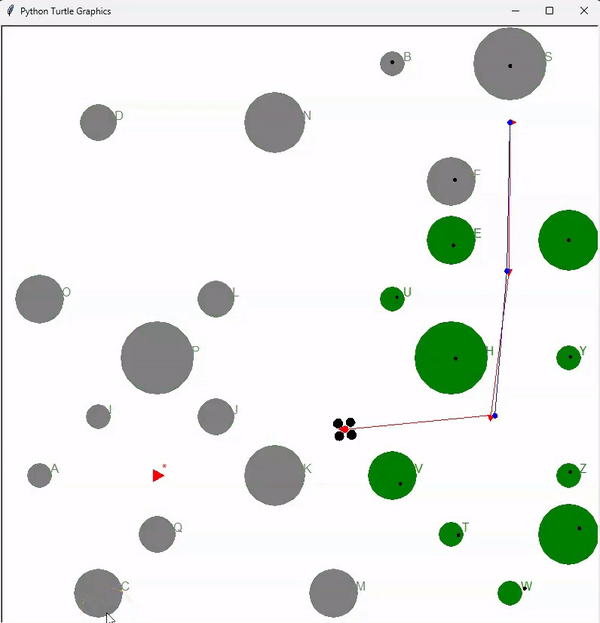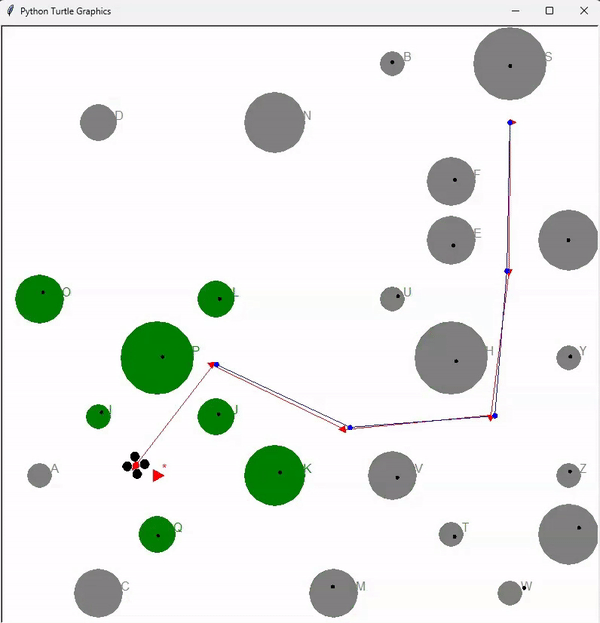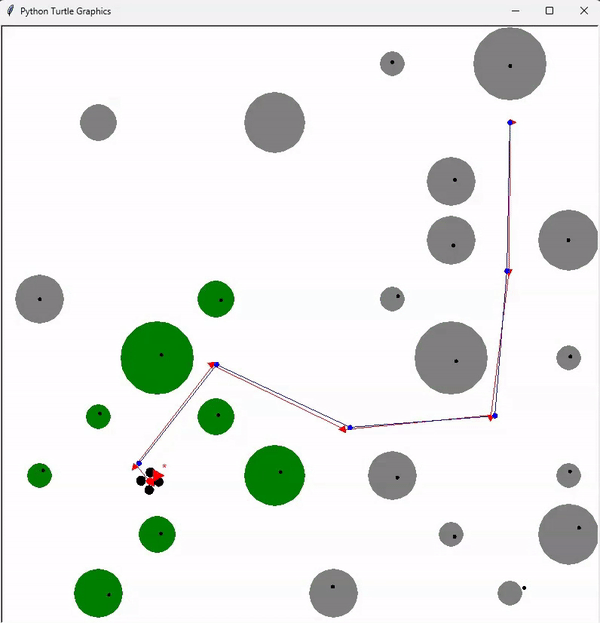
Lastly, a SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) algorithm is implemented, combining both localization and mapping capabilities. The animation below demonstrates an autonomous drone, referred to as an automemos drone, effortlessly navigating through a jungle, skillfully avoiding collisions with trees (represented by green circles). The drone lacks prior knowledge of the tree locations and sizes, hence it maps all the trees by processing lidar sensor information. It simultaneously locates itself within the jungle and ultimately finds the optimal path to the target.
The final animation provides a visualization of the automemos drone autonomously navigating through a jungle, mapping trees, and successfully reaching the target location while avoiding collisions.

Through the integration of these techniques, this project aims to bring us closer to the realization of autonomous vehicles, paving the way for a future where driverless technology is commonplace.